The prostate is a gland below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It plays a key role in the male reproductive system, producing seminal fluid that carries sperm. Below, we examine the types of prostate surgery procedures used to treat enlarged prostates and prostate cancer and improve urinary flow.
Why is prostate surgery performed?
Surgery to remove all or part of the prostate gland is called a prostatectomy. Prostate surgery is most common for prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or an enlarged prostate.
Pre-treatment education is the first step in treatment decision-making. All types of prostate surgery can be done under general anesthesia (where the patient is completely asleep and unconscious) or spinal anesthesia (which numbs the lower half of the body). The doctor will decide on the type of anesthesia based on the patient’s current condition.
Surgery goals include:
- Treating the underlying condition
- Preserving urinary flow (ability to urinate easily)
- Preserving erectile function
- Minimizing side effects
- Minimizing pain before, during, and after surgery
- Enlarged prostate symptoms
- Prostate surgery types
Prostate surgery types
The goal of prostate surgery depends greatly on the patient’s condition. For example, prostate cancer surgery removes cancerous tissue, while surgery for an enlarged prostate removes prostate tissue and restores normal urinary flow.
 Open prostate surgery
Open prostate surgery
 Open prostatectomy
Open prostatectomy
This surgery, also called traditional or open access surgery, is used for prostates over 80 grams. The surgeon makes an incision on the skin surface to remove the prostate and surrounding tissues. This surgery takes about 1.5 hours, with a 2-3-day hospital stay. There are two main types of open access:
Retropubic
The surgeon accesses the prostate by making an incision below the abdomen. In most cases, only the prostate is removed. However, some lymph nodes may be removed for sampling in cancer cases with suspected invasion of the surrounding tissues.
If cancer spreads throughout the body, the surgeon will refrain from continuing surgery and not remove additional involved tissues.
The perineal approach
In this method, the surgeon makes an incision between the rectum and the scrotal sac and removes the prostate gland through that opening. This procedure is often done when the patient has a co-existing condition that prevents the surgeon from using the retropubic approach.
Lymph nodes and lymph ducts cannot be removed in this situation. Surgery time is shorter than the retropubic method, but there is a higher risk of erectile dysfunction.

 Laparoscopic method
Laparoscopic method
The least invasive method of prostate access is laparoscopic surgery. This procedure, lasting about 2-3 hours, still requires further research to become a standard surgical procedure. There are two main methods.
Laparoscopic prostatectomy
This surgery requires very small incisions to insert tiny surgical tools. The inside of the body is viewed through a small tube equipped with a camera.
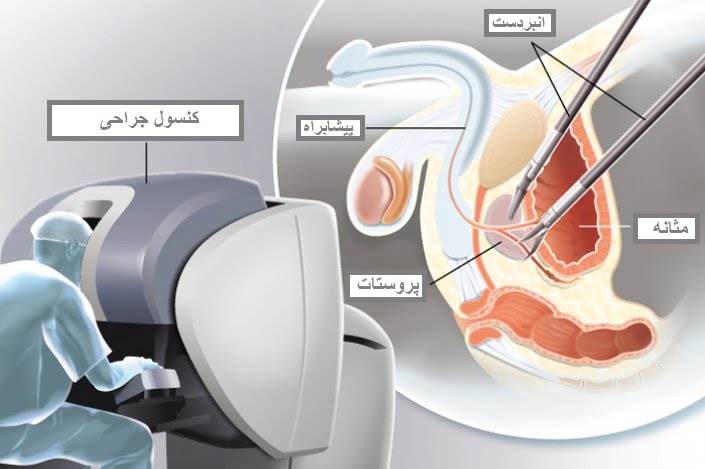
Robotic laparoscopic prostatectomy
The surgeon operates using a robotic arm and monitors connected to the robotic camera without hand intervention. The robotic arm provides greater maneuverability and precision.
There are no major differences between the above surgical methods. However, with robotic laparoscopy, there is typically:
- Less pain
- Short hospital stay
- Faster recovery
- Less blood loss
Also, with the robotic method, faster improvement in bladder control and shorter hospital stay compared to regular laparoscopy is seen.
Types of prostate surgery that maintain urinary flow
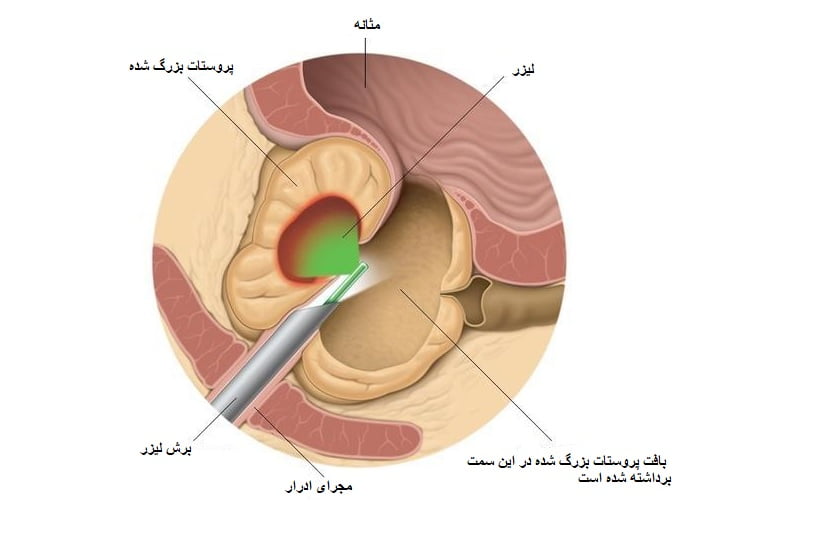
1-Laser prostate surgery
This surgery treats benign prostate enlargement without external incisions. The surgeon inserts a fiberoptic scope through the urethra. In laser surgery, prostate tissue obstructing normal urine flow is cut using a laser.
2-Endoscopic surgery
Similar to laser surgery, no external incisions are made. The surgeon inserts a long, flexible tube through the penis tip, cutting prostate tissue away. This is one of the least invasive prostate surgery methods.
Surgery to widen the urethra
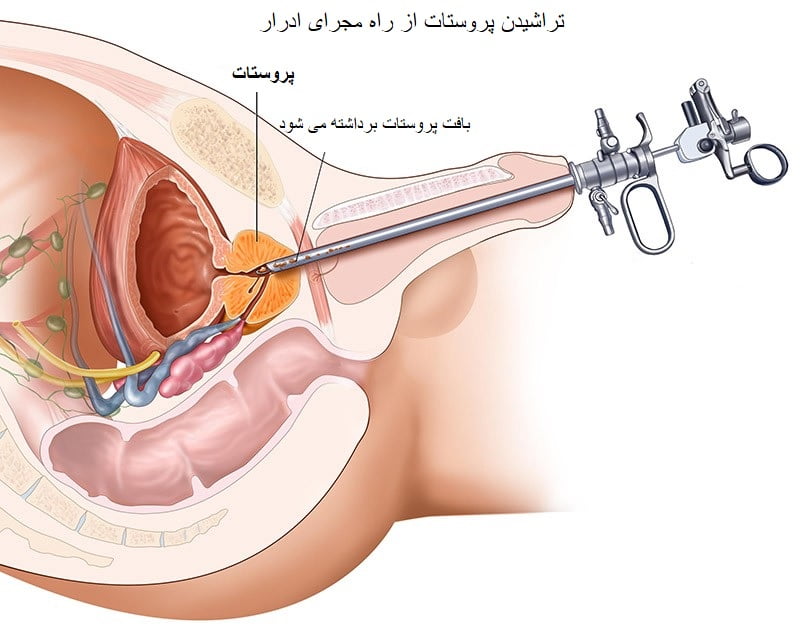
1-Transurethral prostate resection (TURP)
The standard and best surgery for benign prostate hyperplasia is transurethral prostate resection (TURP). Portions of the enlarged prostate are cut using looped wire. They fall into the bladder and are flushed out at the surgery’s end. This 1-hour surgery has a 1-2-day hospital stay.
2-Transurethral prostate incision (TUIP)
This surgery involves small incisions to widen the urethra in the prostate and bladder neck. It is used for prostates under 40 grams (not a validated method) and takes about 30 minutes.
What happens after prostate surgery?
Before ending anesthesia, the surgeon inserts a Foley catheter to allow easier urine drainage from the bladder. This catheter needs to stay in the bladder for 5-7 days.
A hospital stay after surgery is usually just a few days, but the patient can be discharged 24 hours after surgery if there are no issues.
Regardless of surgery type, pain at the incision site remains for a few days. The following symptoms may be seen after surgery:
- Blood in the urine
- Inability to control urination
- Urinary irritation
- Urinary tract infection
- Prostatitis
These symptoms are normal for a few days to weeks after surgery. Recovery time depends on surgery type and duration, the patient’s overall health, and following medical instructions.
General prostate surgery side effects
All surgical methods can have some side effects. These include:
- Reaction to anesthesia
- Bleeding
- Infection at the surgery site
- Organ damage
- Blood clots
- Symptoms indicating infection include fever, chills, swelling, or discharge from the surgical incision site.
- Urinary problems: Pain during urination, difficulty urinating, and urinary incontinence. These typically resolve after two weeks to several months and rarely remain permanently.
- Erectile dysfunction: Not having an erection for 8-12 weeks after surgery is normal. If nerve damage occurs, chances of long-term erectile problems are higher. Some men report a slight shortening of the penis due to a shortened urethra.
- There is a chance of fluid accumulation in the lymph nodes in the groin or legs or progression to an inguinal hernia. This can cause pain and swelling, although both can be treated.
What should be done after prostate surgery?
- Keep the surgical wound clean.
- Do not drive for one week.
- Do not exercise for six weeks.
- Avoid stairs if possible.
- Avoid hot tubs and swimming pools.
- Change the sitting position every 45 minutes.
- Use the recommended treatments to reduce pain.
- Also, bowel movements 2-3 days after surgery are important. Drink fluids, add fiber to meals, and exercise lightly to prevent constipation.
- Avoid bladder irritants like spices, seasonings, citrus, and acidic foods to prevent painful urination and better control urination.

 Open prostate surgery
Open prostate surgery